How To Find Mean Median And Mode From A Histogram
How to find the median
Published on October 2, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.
The median is the value that's exactly in the middle of a data set when it is ordered. It's a measure of central tendency that separates the lowest 50% from the highest 50% of values.
The steps for finding the median differ depending on whether you have an odd or an even number of data points. If there are two numbers in the middle of a data set, their mean is the median.
The median is usually used with quantitative data (where the values are numerical), but you can sometimes also find the median for an ordinal data set (where the values are ranked categories).
We'll walk through steps using a small sample data set with the weekly pay of 5 people.
| Weekly pay (USD) | 350 | 800 | 220 | 500 | 130 |
|---|
Step 1: Order the values from low to high.
| Weekly pay (USD) | 130 | 220 | 350 | 500 | 800 |
|---|
Step 2: Calculate the middle position.
Use the formula (n + 1) / 2, where n is the number of values in your data set.
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| (n + 1) / 2 | n = 5 (5 + 1) / 2 = 3 |
The median is the value at the 3rd position.
Step 3: Find the value in the middle position.
| Weekly pay (USD) | 130 | 220 | 350 | 500 | 800 |
|---|
The median weekly pay is 350 US dollars.
In an even-numbered data set, there isn't a single value in the middle of the data set, so we have to follow a slightly different procedure.
Let's add another value to the data set. Now you have 6 values.
| Weekly pay (USD) | 350 | 800 | 220 | 500 | 130 | 1150 |
|---|
Step 1: Order the values from low to high.
| Weekly pay (USD) | 130 | 220 | 350 | 500 | 800 | 1150 |
|---|
Step 2: Calculate the two middle positions.
The middle positions are found using the formulas n / 2 and (n / 2) + 1, where n is the number of values in your data set.
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| n / 2 | n = 6 6 / 2 = 3 |
| (n / 2) + 1 | n = 6 (6 / 2) + 1 = 4 |
The middle values are at the 3rd and 4th positions.
Step 3: Find the two middle values.
| Weekly pay (USD) | 130 | 220 | 350 | 500 | 800 | 1150 |
|---|
The middle values are 350 and 500.
Step 4: Find the mean of the two middle values.
To find the median, calculate the mean by adding together the middle values and dividing them by two.
The median weekly pay for this data set is is 425 US dollars.
What is your plagiarism score?
Compare your paper with over 60 billion web pages and 30 million publications.
- Best plagiarism checker of 2020
- Plagiarism report & percentage
- Largest plagiarism database
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
The median is usually used for quantitative data, which means the values in the data set are numerical. But you can sometimes also identify the median for ordinal data.
Ordinal data is organized into categories with a rank order – for example language ability level (beginner, intermediate or fluent) or level of agreement (strongly agree, agree, etc).
The process for finding the median is almost the same.
Odd-numbered data set
We'll walk through the steps for an odd-numbered ordinal data set with 7 values.
You categorize reaction times of participants into 3 groups: slow, medium or fast.
First, order all values in ascending order.
| Reaction speed | Slow | Slow | Medium | Medium | Fast | Fast | Fast |
|---|
Next, find the middle value using (n + 1) / 2, wheren is the number of values in the data set.
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| (n + 1) / 2 | n = 7 (7 + 1) / 2 = 4 |
The median is the value at the 4th position.
| Reaction speed | Slow | Slow | Medium | Medium | Fast | Fast | Fast |
|---|
The median reaction speed is Medium .
Can you find the median for an even-numbered ordinal data set?
The mean cannot be calculated for ordinal data, so the median can't be found for an even-numbered data set.
For example, if the two middle values are "slow" and "medium," you can't calculate the mean of these values.
In practice, ordinal data is sometimes converted into a numerical format and treated like quantitative data for the sake of convenience. Then the mean of the middle values can be calculated to find the median.
While this is considered acceptable in some contexts, it is not always seen as correct.
The median is the most informative measure of central tendency for skewed distributions or distributions with outliers.
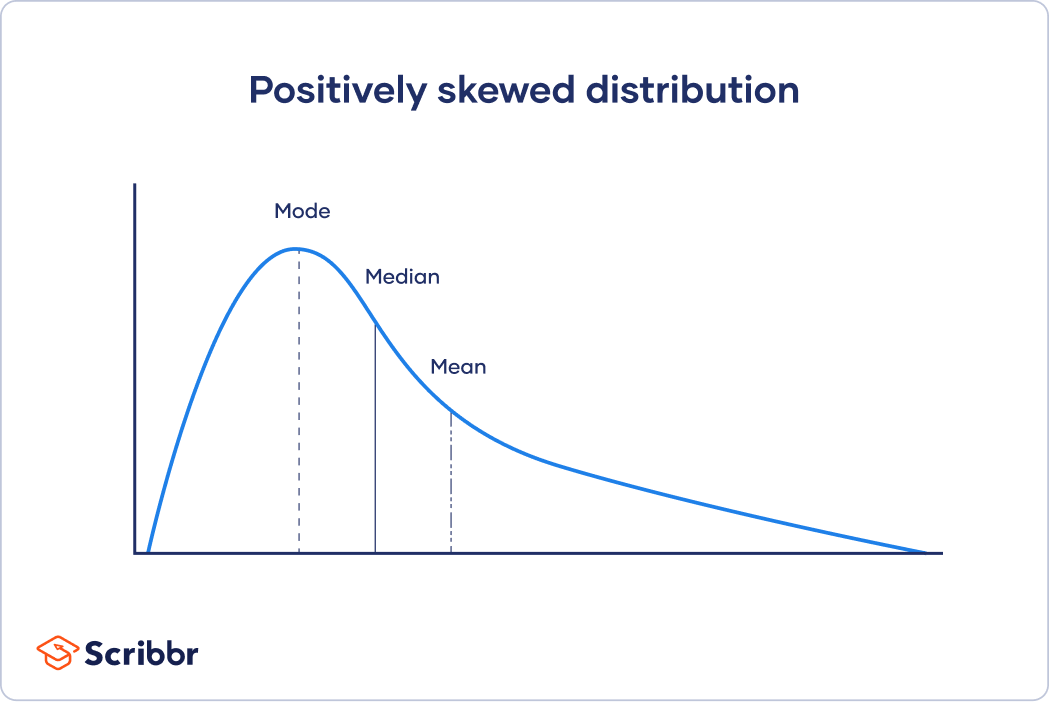
In skewed distributions, more values fall on one side of the center than the other, and the mean, median and mode all differ from each other.
In a positively skewed distribution, there's a cluster of lower scores and a spread out tail on the right.
In a negatively skewed distribution, there's a cluster of higher scores and a spread out tail on the left.
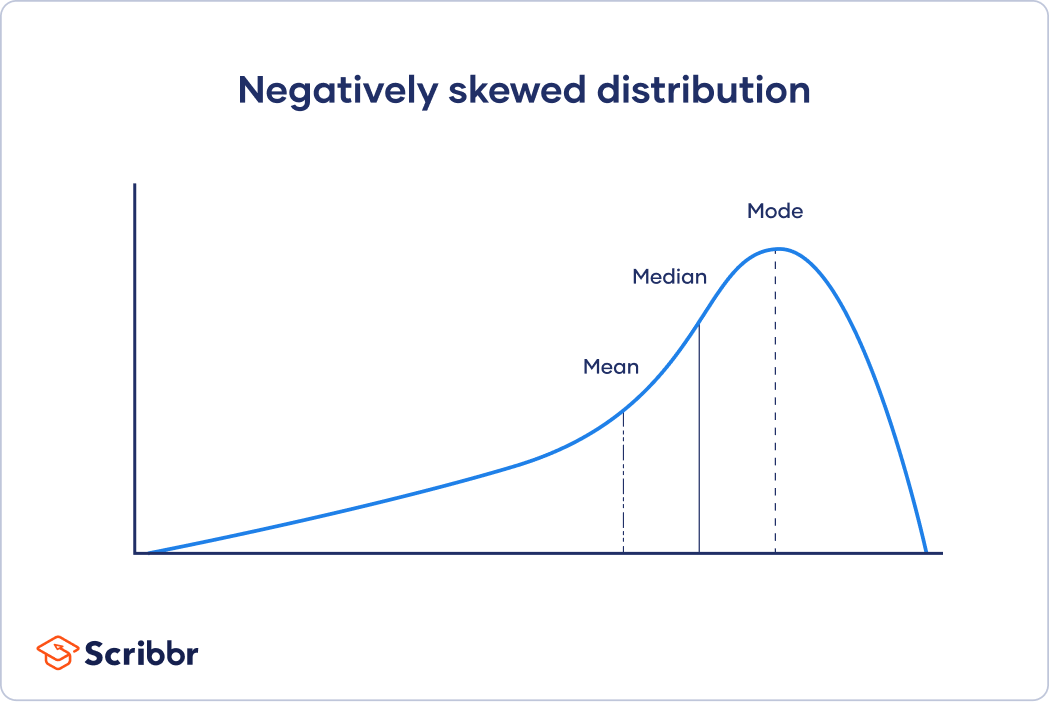
Because the median only uses one or two values from the middle of a data set, it's unaffected by extreme outliers or non-symmetric distributions of scores. In contrast, the positions of the mean and mode can vary in skewed distributions.
For this reason, the median is often reported as a measure of central tendency for variables such as income, because these distributions are usually positively skewed.
The level of measurement of your variable also determines whether you can use the median. The median can only be used on data that can be ordered – that is, from ordinal, interval and ratio levels of measurement.
- How do I find the median?
-
To find the median, first order your data. Then calculate the middle position based on n, the number of values in your data set.
- Ifn is an odd number, the median lies at the position (n + 1) / 2.
- Ifn is an even number, the median is the mean of the values at positions n / 2 and (n / 2) + 1.
- When should I use the median?
-
The median is the most informative measure of central tendency for skewed distributions or distributions with outliers. For example, the median is often used as a measure of central tendency for income distributions, which are generally highly skewed.
Because the median only uses one or two values, it's unaffected by extreme outliers or non-symmetric distributions of scores. In contrast, the mean and mode can vary in skewed distributions.
Is this article helpful?
You have already voted. Thanks :-) Your vote is saved :-) Processing your vote...
How To Find Mean Median And Mode From A Histogram
Source: https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/median/
Posted by: hugginssaingestur.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Find Mean Median And Mode From A Histogram"
Post a Comment